Strive towards Net-Zero emissions with recovery of all waste heat on Montpellier R&D site
Sanofi has implemented waste heat recovery facilities at its R&D site in Montpellier, France in partnership with Dalkia, which has reduced the site’s gas…

Reduce the site's energy consumption and associated CO2 emissions by recovering the heat produced during the production of chilled water for re-use in the heating hot water networks.
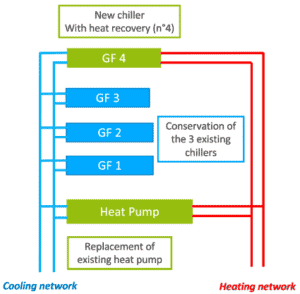
The principle of low-temperature heat recovery is one of the priorities of Sanofi’s decarbonization approach. The project involves removing the old heat pump and replacing it with a new heat recovery chiller that uses modern technology (magnetized bearings). The improvements have the following specific effects on how the site produces chilled water and heating hot water:
Originally, the system consisted of the following equipment:
– A heat pump (Heat pump) that operates continuously to produce chilled water and hot water.
– The three current chillers (GF1, GF2 and GF3) take over to produce cold water in addition to the production of the heat pump. The chillers are switched on one after the other with an operating order that ensures an equivalent annual operating time between each chiller.
– A steam-water exchanger located in LYG3, fed by the steam produced by the boiler in operation, which provides additional power for the production of hot water. This equipment currently supports the heat pump in order to produce the hot water necessary for heating the premises, mainly in winter. Thus, the overall production of cold water provided by this energy installation is intended to supply equipment such as air handling units (AHU), water loop exchangers, air conditioning cassettes, etc.
– As for the production of hot water, it is mainly produced by the heat pump with, if necessary, the LYG3 exchanger as a support in order to heat the premises of the whole establishment (via AHU and air conditioning cassettes).
– The project incorporates a new heat pump (620 kWp and 820 kW hot TFP) that will replace the existing equipment and operate to produce both chilled and hot water. This new equipment will be more energy efficient.
– A new GF4 chiller (1414 kWp and 950 kW hot) which will be more efficient than the current equipment and will contribute to the production of cold water for the Sanofi Genzyme facility and will be equipped with a heat recovery system. Thus, via heat recovery, the GF4 will contribute to the production of hot water for the site. This new operation will make it possible to stop using the current steam exchanger during the winter period and thus reduce the consumption of gas from the boilers (carbon neutrality objective to ensure the global heating of the establishment).
– The three current chillers (GF1, GF2 and GF3) will take over to produce additional cold water.
– The two new units, TFP and GF4, will be equipped with an HFO type R1234ze refrigerant (the previous TFP was initially equipped with an R134A fluid).
The project (1.221 M€) was financed by the Energy Savings Certificates (CEE) up to 1.045 M€ and was carried by Engie (Equans) for CEE. This waste heat recovery facility is fully operational since December 2021.
on which the project has a significant impact
Scope 1 – Substitution of R134a refrigerant by HFO R1234 ze with 200 times lower GWP.
Scope 2 – Recovery of heat from the new cold group GF4 to heat the building instead of using the steam exchanger and gas boilers.
Greater electrical efficiency from the new TFP and GF4.
Based on the facility’s 2019 consumption data and the outlook for increased activity, it was estimated that the project would result in the following consumption reductions: 738 MWh/year of electricity and 429 MWh/year of natural gas. These estimates resulted in a projected emission reduction of 109 tCO2/year (conversion factor for nuclear energy and natural gas).
Project amount of 1,221 M€:
- Financing from the CEE at a level of 1,045 M€
- Financing provided by Sanofi up to €176,000.
October 2020 : Study phase
Sanofi Lyon Gerland, 23 bd Chambaud de la Bruyère 69007 LYON
Replicability target: The target scope includes all French sites where a plan with a strong enough subsidy structure makes the project financially feasible.
The implementation of this project should make it possible to reduce the use of the site’s gas boilers and eliminate the possibility of using the vapor exchanger.
RAS – project purchasing
Aymeric VIGNON aymeric.vignon@sanofi.com

Sanofi has implemented waste heat recovery facilities at its R&D site in Montpellier, France in partnership with Dalkia, which has reduced the site’s gas…